Introduction
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is a widely-used single sign-on (SSO) protocol that enables secure authentication between an Identity Provider (IdP) and a Service Provider (SP) using signed XML assertions.
SAML is common in enterprise setups, federated identity management, and cloud/SaaS access.
🧭 Step-by-Step Breakdown
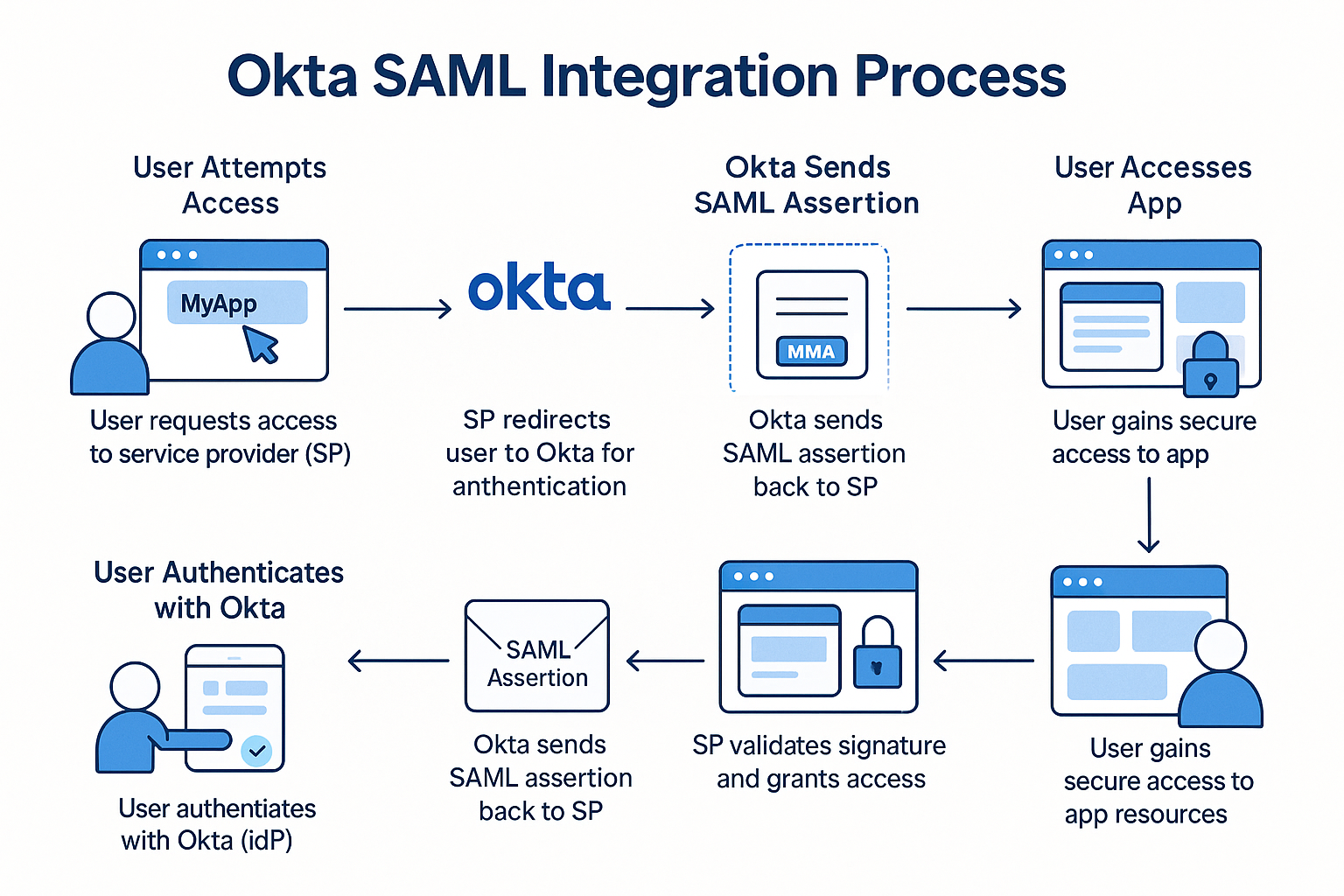
1. User Attempts to Access a Protected Resource
- The user opens a browser and requests a resource on the Service Provider (SP).
- The SP determines that the user is not authenticated.
2. SP Initiates SAML Authentication Request
- The SP redirects the user’s browser to the Identity Provider (IdP) using a SAML AuthnRequest.
- The request is typically:
- Base64-encoded
- Sent via HTTP Redirect or POST binding
- Includes:
- SP Entity ID
- ACS (Assertion Consumer Service) URL
- Requested authentication context
3. User Authenticates at Identity Provider
- The IdP presents a login screen (username/password, MFA, etc.).
- If credentials are valid, authentication is successful.
4. IdP Issues a SAML Assertion
- The IdP generates a SAML Response, containing:
- Signed SAML Assertion
- User identity (NameID)
- Optional attributes (email, roles, etc.)
- The response is signed using the IdP’s private key for integrity and authenticity.
5. SAML Response Sent to SP
- The browser auto-submits a form back to the SP’s ACS URL (via HTTP POST).
- The SP validates:
- Signature
- Audience
- Timestamps
- Destination URL
6. User Is Granted Access
- If everything checks out, the SP creates a session for the user.
- The user is now authenticated and redirected to the originally requested resource.
🔐 Key Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| IdP | Identity Provider (e.g., Okta, ADFS, Azure AD) |
| SP | Service Provider (e.g., Salesforce, Dropbox, internal web app) |
| SAML Assertion | XML token containing authentication and user info |
| ACS URL | Endpoint on SP that receives SAML response |
✅ Benefits of SAML
- 🌐 Single Sign-On (SSO) across multiple domains/apps
- 🔏 Federated Identity — centralizes user credentials at IdP
- 🔐 Secure — signed assertions, optional encryption
- 🧾 Attribute Sharing — pass roles, email, groups, etc.
🔚 Conclusion
SAML is a battle-tested protocol for enabling enterprise-grade SSO and identity federation. It’s ideal when your organization uses a centralized IdP and wants to securely authenticate users across multiple SPs.
For more identity & access security tutorials, Visit IDAMworks.com for guides and integration support.